To get your content into AI-generated answers, you must stop thinking about ranking and start thinking about getting cited. The goal is no longer a blue link; it's being the source inside the AI answer. This means building your content so AI models can easily grab, understand, and present it as the most authoritative fact on a topic.
You need to become the answer itself.
The New Reality: AI Overviews Are Here to Stay
The ground is shifting fast. AI Overviews aren't a future concept—they're live, fundamentally changing how search results work. This is a direct threat to traffic, as AI summaries often give users the answer they need without them ever needing to click through to your site. The old SEO playbook is being torn up.
This isn't just a theory. According to a 2024 analysis by SEOclarity, AI Overviews now appear in 13.14% of all Google queries. Even more concerning, these answers can slash clicks to websites by a massive 34.5%.
And where are these AI answers coming from? Over 76% of citations are pulled from pages that are already in the top 10. The coveted #1 spot just isn't what it used to be.
This table breaks down the strategic shift. It's not about abandoning old principles but adapting them for a new, AI-first reality.
Traditional SEO vs. AI Search Optimization
| Focus Area | Traditional SEO Approach | AI Search Optimization Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Rank #1 on the SERP | Become a cited source in the AI Overview |
| Content Structure | Long-form, narrative-driven content | Clear, factual, and machine-readable snippets |
| Keywords | Focus on a primary keyword and its variants | Focus on conversational prompts and user intent |
| Success Metric | Organic traffic and keyword rankings | AI citations and Share of Voice (SOV) |
| Authority Signals | Backlinks, domain authority | E-E-A-T, factual accuracy, structured data |
| Competition | Other websites ranking for the same keywords | The AI answer box itself |
The biggest takeaway is the mindset change. You're no longer just competing with other websites; you're competing for the AI's attention.
Your New Competitor Is the Answer Box
For years, we obsessed over outranking competitors. Now, the biggest competitor is the AI-generated answer box that sits above everything else. If you're not cited in that box, you're invisible for a huge number of searches. Getting featured there is the new #1 ranking.
This is especially true for informational queries where people are looking for quick answers, like "best software for project management" or "how to fix a leaky faucet." The AI gives them a neat summary, and the incentive to click through to five different articles just disappears. As this becomes more common, understanding new strategies like generative engine optimisation services is no longer optional.
Mini Case Study: Writing for Machines vs. Writing for People
Imagine two tech blogs both writing about the "best noise-canceling headphones."
- Blog A uses a creative, narrative approach. The article is full of flowery headings like "Silence the World" and "A Symphony for Your Ears." All the important specs are buried deep inside long paragraphs.
- Blog B takes a direct route. It uses clear H2s like "Key Features of the Sony WH-1000XM5" and puts technical data into a simple comparison table. It even adds an FAQ section answering specific questions like "How does active noise cancellation work?"
When a user asks an AI, "Which headphones have the best battery life and noise cancellation?" the model can instantly parse the structured information from Blog B. It will pull the exact numbers from the table and the clear explanation from the FAQ, citing Blog B as the source.
Blog A, despite being a great read for humans, is completely invisible to the AI. Its information isn't machine-readable.
This scenario gets to the heart of the new challenge: You have to write for both human readers and machine parsers. The good news is that well-structured, clear content works brilliantly for both. Knowing how to rank in Google’s AI-driven results is all about adapting your strategy to this new reality. The fundamentals of authority and quality haven't gone away, but they now need to be packaged in a way that an AI can process with absolute confidence.
Decode Conversational Prompts, Not Just Keywords
Keyword research isn't what it used to be. To get your content seen and cited by AI, you have to ditch the old habit of chasing short, choppy keywords and start thinking in conversational prompts.
People don't type "best CRM software" into a chatbot. They ask, "What's the best CRM for a small sales team of 5 people that integrates with Slack and is easy to learn?"
That's a whole different ballgame. It’s not just one keyword; it’s a detailed problem statement loaded with multiple layers of intent. Your job is to break that prompt down and serve up an answer so precise that an AI model flags it as the most complete and authoritative source on the web.
This shift means your research process has to change. Forget just looking at search volume. You need to get to the heart of the actual conversational questions your audience is asking.
Find the Real Questions Your Audience Is Asking
Your traditional keyword tools can still give you a starting point, but they won't show you the full picture. You've got to dig a lot deeper into the why behind the search.
Here are a few practical ways to find these conversational gems:
- Mine 'People Also Ask' (PAA) boxes: These are a goldmine for discovering related questions. Tools like AlsoAsked are great for visualizing these PAA relationships, letting you see the branching logic of a user's entire thought process. This is how you build out comprehensive topic clusters that AI loves.
- Scour community forums: Get into Reddit, Quora, and any industry-specific forums where your audience hangs out. Pay close attention to the exact phrasing people use when they're describing their problems. They are literally handing you the prompts you need to target.
- Interview your sales and support teams: These folks are on the front lines, hearing your customers' real questions every single day. Just ask them for the top 10 most common problems or questions they have to answer.
Once you have a solid list of these conversational prompts, the real work begins: breaking them down into their core components. This is what allows you to structure your content to answer every single part of the user's need.
Every complex AI prompt can be deconstructed into three parts: the problem, the desired format, and the expected outcome. Answering all three is the key to getting cited.
A Framework for Deconstructing Intent
Let's walk through a real-world example. Imagine a SaaS company that sells project management software. A potential customer might ask an AI something like this:
"Compare Asana and Monday.com for a marketing agency managing multiple client campaigns. I need to see a feature and pricing breakdown."
Here’s how you deconstruct that prompt:
- The Underlying Problem: The user runs a marketing agency and is struggling to manage multiple client campaigns. They need a system to get organized and work more efficiently.
- The Desired Format: The user was crystal clear. They asked for a comparison, a feature breakdown, and a pricing breakdown. A long, narrative-style article just won't cut it here. They want structured, scannable data, most likely in a table.
- The Expected Outcome: The user wants to make a confident, informed decision about which tool will solve their agency's specific workflow headaches.
Your content has to hit all three of these elements head-on. Don't just write another generic "Asana vs. Monday" post. Create a specific section with a clear H3 heading like "Asana vs. Monday for Marketing Agencies" and use a comparison table to break down the features that actually matter for campaign management.
To truly master this, it's also crucial to understand how AI is used to create personalized experiences on a broader scale. For more on this, you can explore how AI enhances personalization in DXPs.
Mini Case Study: Engineering Content for a Specific Prompt
Let's look at a B2B software review site that wants to capture traffic for prompts about accounting software.
-
The Old Way: They publish a massive article targeting "best accounting software for small business." It's just a long, generic list with basic descriptions. It might rank okay in traditional search, but it never, ever gets cited by AI.
-
The AI-Optimized Way: After doing their research, they uncover a common conversational prompt: "Which accounting software is best for a freelance graphic designer who needs to track project expenses and send invoices?"
So, they create a highly specific section within their larger article, titled "Best Accounting Software for Freelancers." Inside that section, they include a small table comparing QuickBooks Self-Employed and FreshBooks, but they only focus on the features relevant to freelancers, like mileage tracking, invoice customization, and expense categorization.
The result? When an AI model gets this prompt, it finds a perfectly structured, self-contained answer that directly addresses the user's specific profession and needs. The site gets the citation because its content was engineered for the prompt, not just the keyword.
This targeted, surgical approach is how you win in AI search. It’s not about covering everything under the sun; it’s about providing the absolute best, most specific answer to a well-defined problem.
Structure Your Content for Machine Readability
AI models don’t read content; they parse it. A dense wall of text is practically invisible to a machine trying to pull a clean, factual answer. If you want to optimize for AI search, you have to start thinking like an engineer. Your job is to structure the page so every key point is machine-readable and easy to grab.
This isn't about dumbing down your content. It's about organizing it with a logical, hierarchical flow that signals clarity and authority to AI systems.
Think about the user's journey. Your content structure should mirror their intent, from the initial problem to the desired outcome.
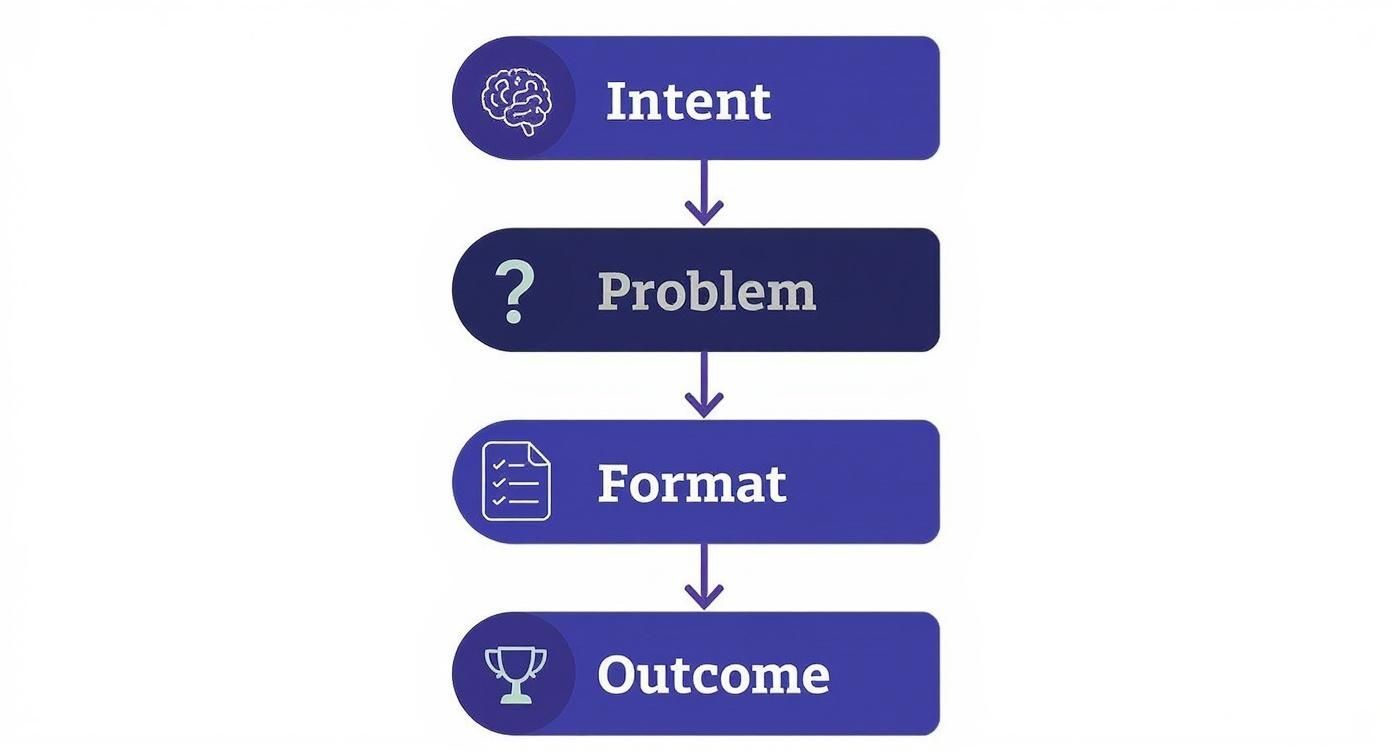
This framework shows that your content needs to directly address the user’s problem, deliver the answer in their preferred format, and guide them toward a specific outcome. A good structure does all three.
Use Headings as a Logical Roadmap
Your headings (H2s and H3s) are the single most important structural element for AI. They create a table of contents, breaking your article into distinct, understandable chunks. Vague headings like “Key Details” are useless.
Instead, frame your headings as descriptive, question-based signposts that an AI can easily match to a user's prompt.
- Weak Heading: "More Information"
- Strong Heading: "How Does On-Page SEO Affect AI Citations?"
That simple change turns a generic section into a citable answer. It creates a self-contained block of information that an AI can lift directly into a generated response because the heading clearly defines what's inside.
Create Self-Contained Snippets
AI models love to pull small, self-contained “nuggets” of information. Your goal is to create these nuggets throughout your content. Each one should make perfect sense even when ripped out of its original context.
Ask yourself this: could a single paragraph, list, or table from your article stand alone as a complete answer? If the answer is no, it’s not optimized for AI.
Blockquotes, concise lists, and summary tables are perfect for this. They package information into a format that is inherently easy for a machine to identify, parse, and repurpose for an AI-generated summary.
A product review site, for example, could use a simple table to compare key features. This is far more valuable to an AI than burying those same details in a long, narrative paragraph. An AI can instantly extract the structured data from the table to answer a comparative prompt.
Implement Schema for Unambiguous Context
Schema markup is the ultimate cheat sheet you can give to an AI. It’s a layer of code that explicitly tells search engines and AI models what your content is about, removing all the guesswork.
While there are hundreds of schema types available, a few are particularly powerful for earning AI citations:
- FAQPage Schema: Explicitly marks question-and-answer sections, making them prime candidates to be pulled into AI answers.
- HowTo Schema: Breaks down step-by-step instructions into a clear, sequential format that machines can easily follow and present.
- Product Schema: Defines key attributes like price, availability, and review ratings in a structured way.
Implementing schema is like putting bright, clear labels on your content. It helps an AI understand the type of information you're providing, which greatly increases its confidence in using your content as a source. The official documentation at Schema.org provides a full list of types.
To get a better sense of what these AI systems actually "see" when they parse your page, you can check out a detailed breakdown of what ChatGPT sees on your page.
Real-World Example: A B2B SaaS Blog
Let's compare two approaches for a blog post titled "How to Choose a CRM."
Company A (Poor Structure): The article has a single H1 and then a 2,000-word wall of text. It covers everything but lacks any real structure. Key features are explained in long paragraphs, and pricing is mentioned casually within the text. An AI would struggle to extract any specific facts from this.
Company B (Excellent Structure): The article is meticulously structured to be machine-readable.
- It uses clear H2s like "Key CRM Features for Sales Teams" and "Comparing CRM Pricing Models."
- Under each feature, an H3 is used, such as "Lead Scoring Capabilities," followed by a tight, two-sentence explanation.
- A dedicated section uses
FAQPageschema to answer common questions like "What is the average cost of a CRM per user?" - A comparison table summarizes the top 3 CRMs, with columns for "Best For," "Price," and "Key Feature."
Company B's content is engineered to be cited. An AI can easily grab the answer to "average cost of a CRM" from the FAQ schema or pull the comparison data directly from the table. This structured approach makes their content the perfect source for a detailed, multi-faceted AI-generated answer.
Build Verifiable Authority and Trust Signals
In AI search, trust isn't a feeling; it's a technical signal. AI models are trained to sniff out and avoid misinformation, so they’re constantly hunting for content from authoritative sources. If your content doesn't send the right signals, it's invisible—no matter how well-written it is.
To get your content noticed and cited by AI, you have to build and display authority in a way that machines can actually verify. This goes way beyond the vague concept of E-E-A-T and into concrete, machine-readable actions.

This shift is happening much faster than most marketers think. By 2026, traditional search engine volume is expected to drop by a massive 25% as users move to AI assistants. Nailing this is non-negotiable. For some sites, AI-driven referrals from tools like ChatGPT and Perplexity are already sending more traffic than Reddit and LinkedIn combined.
Demonstrate Firsthand Experience
AI models are getting impressively good at telling the difference between genuine, hands-on expertise and generic, affiliate-style fluff. Demonstrating firsthand experience is one of the strongest trust signals you can possibly send.
Think about it from the AI's perspective. It's trying to answer, "Is HubSpot CRM good for a small startup?" and has two articles to pull from:
- A generic affiliate blog: The post just lists features copied from HubSpot's website and shoves an affiliate link at the end. There's zero real-world application.
- A SaaS marketing blog: The author includes screenshots of their own HubSpot dashboard, walks through a specific workflow they actually built, and shares the measurable results it generated for their team.
The AI will cite the second source every single time. Why? Because the specific details, unique screenshots, and hard-to-fake insights are verifiable proof of experience. A content farm simply can't replicate that.
Establish Clear Author Credentials
Anonymous content is a huge red flag for AI. Every single piece of content needs a clear author with a detailed bio page linked directly from their name.
An author bio isn't just for show; it's a data source for the AI. It should explicitly state the author's credentials, experience, and qualifications related to the topic.
Your author pages need to function as a central hub of authority.
- List credentials and experience: Get specific. Mention roles, companies, and years of experience (e.g., "10+ years in B2B SaaS marketing").
- Link to other authoritative profiles: Connect out to the author's LinkedIn, industry publications they've written for, or their speaker page for relevant conferences.
- Use Author Schema: This is critical. Implement
Personschema markup on the author page to explicitly tell AI systems who the author is and what their expertise is.
This creates a web of connections that reinforces the author's credibility, making their content a far more reliable source for an AI to cite. You can see how these signals get measured by digging into the best citation analysis options for optimizing AI search.
Cite Credible External Data
Just like in academia, citing your sources builds trust. When you make a claim or present a statistic, link out to the original, authoritative source. This proves to an AI that your information is well-researched and not just pulled out of thin air.
- Prioritize primary sources: Always try to link directly to academic studies, government data, or official company reports.
- Avoid citing competitors directly: That’s just bad form. Instead, reference neutral, third-party sources like established industry publications or market research firms.
- Attribute quotes and data clearly: Don't just drop a link. Mention the source by name in the text itself (e.g., "According to a 2024 report from Forrester...").
This practice positions your content as a trustworthy curator of information, which dramatically increases the odds that an AI will use it as a foundational source for its own answers.
How to Measure Your AI Search Performance
Optimizing content for AI without measuring your impact is just guessing. You can't rely on your old SEO toolkit here. Rank trackers and Google Search Console are completely blind to whether you're showing up in AI Overviews or a ChatGPT response.
So, you need a new, more hands-on approach. The good news is that you can build a practical framework for testing and measuring your success right now. It all comes down to manually checking your content's visibility and tracking your "Share of Voice" in this new AI-driven world.
This isn't just a side task; it's a core part of a winning strategy. In fact, a staggering 86% of SEO experts are already integrating AI tools into their workflows, with many seeing real performance lifts from AI-driven on-page SEO. The next logical step is measuring that performance where it counts—directly inside the AI systems. You can find more details in the latest AI SEO statistics on seoprofy.com.
Manually Test Your Visibility Across Platforms
The most direct way to see what's working is to act like your target customer. This means firing up different AI models and asking them the same conversational questions you're trying to rank for. Don't just check one; you need to test across the major platforms your audience is actually using.
- Google's AI Overviews: Start here. Test your most important informational queries directly in Google to see if you're cited in the generated answer.
- ChatGPT: As a dominant player, it's absolutely crucial to know if your brand is being mentioned and how it's sourcing its information.
- Perplexity: This "answer engine" is a huge source of AI-driven referral traffic and is built on citing its sources clearly.
- Gemini and Claude: Round out your testing with these models to get a broader view of your visibility across the entire ecosystem.
For every prompt you test, you're not just looking for a link. You're hunting for direct citations, brand mentions, and snippets of your content being woven into the answer. This manual process gives you the ground truth.
Here’s a perfect example of a query in Perplexity, which clearly shows its sources. You can see how important a direct citation is—users can immediately see and verify where the information is coming from.
Track Your AI Share of Voice
Share of Voice (SOV) used to be about how often you landed on page one. Not anymore. In the world of AI search, it's about how frequently your brand is cited as a source compared to your competitors for a core set of prompts.
Your goal is to document every single citation. A simple spreadsheet is all you need to get started. This creates a powerful feedback loop that will inform your entire effort to optimize content for AI search.
Here’s a simple framework you can steal for your tracking document:
| Prompt Tested | AI Platform | Your Brand Cited? (Yes/No) | Competitors Cited | Key Insight from Answer | Action Item |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| "best crm for saas startups" | Perplexity | No | HubSpot, Salesforce | Cited a HubSpot blog post comparing CRMs | Create a more specific "HubSpot vs. Us" comparison page |
| "how to calculate customer LTV" | ChatGPT | Yes | None | Pulled the exact 5-step process from our guide | Boost internal links to this guide from related articles |
| "is [Your Product] good for enterprise?" | Gemini | Yes | Mentions a G2 review | Used a quote from a positive G2 review | Add customer testimonials to the enterprise product page |
This process does more than just track progress; it uncovers critical content gaps and competitive opportunities. If a competitor is consistently getting cited for a topic, dig into their content. Find out why. Is their data fresher? Is their page structure more machine-readable? You can then use tools like our AI SEO Tracker to automate this process and scale your insights once you've proven the model.
Mini Case Study: Uncovering a Critical Content Gap
A B2B software company was creating a ton of content around "project management for remote teams," but they had no idea if it was actually working.
Their SEO manager started manually testing prompts in ChatGPT and Perplexity and quickly made a key discovery. For the prompt, "Compare Asana vs. Trello for remote software teams," competitors were cited constantly, but their brand was nowhere to be found. The AI answers consistently pulled from pages with clear, static pricing tables.
Their own pricing? It was hidden behind a "Request a Demo" button, making it completely invisible to AI models. That single insight led them to create a public pricing page with a detailed feature comparison table. Within a few weeks, they started showing up as a cited source for high-intent comparison prompts, directly impacting their visibility and leads. This is a perfect example of how manual testing can uncover hidden roadblocks that traditional SEO tools will always miss.
Your Next Steps for AI Search Optimization
Adapting to this new reality brings up a lot of questions. Marketers and SEOs are scrambling to figure out where to focus their energy as the old rules get rewritten. Here’s how you can take action today.
Does Traditional SEO Still Matter?
Yes, but it's now the foundation, not the entire building. Core SEO principles like crawlability, mobile-friendliness, and a logical internal linking structure are non-negotiable. AI models can't cite what they can't find or access. If your site is a technical mess, you're invisible from the start.
That said, just having good technical SEO isn't enough anymore. You have to layer AI-specific optimizations—like structured data, citable snippets, and clear authority signals—on top of that foundation.
Think of traditional SEO as the ticket to the game; AI optimization is how you actually score.
Should I Create New Content or Update Old Posts?
It’s a mix of both, but start by auditing and updating your existing, high-potential content. Your most authoritative pages already have signals (backlinks, traffic) that you can build on. The real win comes from retro-fitting them for machine readability.
Here’s a quick framework for deciding:
- Update First: Pinpoint your top-performing informational content. Go back in, restructure it with clear headings, add FAQ schema, and break down long paragraphs into concise, citable snippets and tables.
- Create New: Focus new content creation on filling the competitive gaps you find while tracking your AI performance. If a competitor consistently gets cited for a prompt you don't cover, that’s a flashing neon sign telling you to build a dedicated, highly-structured page to win that citation.
How Do I Handle Information Behind a Login or Paywall?
This is a huge challenge. The simple truth is that AI models generally cannot access content that requires a login or subscription. If your most valuable data is locked away, it’s invisible and can't be used as a source for generative answers.
You have to find a balance between protecting your premium content and signaling your authority.
The best approach is to create a public-facing summary or "teaser" version of the gated content. This page can present key findings, data points, or takeaways in a structured, machine-readable format while encouraging users to sign up for the full version.
This hybrid model lets AI find and cite your core insights, driving awareness and traffic, while still preserving the value of your gated assets.
Mini Case Study: Making Gated Content Visible to AI
A financial analytics firm used to publish its most valuable market research as downloadable PDFs behind a strict registration wall. As a result, they had zero visibility in AI-generated answers about their industry. All that deep expertise was completely hidden.
The Fix: They created a public blog post for each major report. Each post summarized the top 3-5 key findings in a bulleted list and included a machine-readable table with a few high-level statistics. A clear call-to-action then prompted users to download the full PDF for the complete dataset.
Within a month, their blog posts started getting cited in AI Overviews for queries like "key trends in fintech 2024." They successfully signaled their authority to the AI without giving away all their proprietary data for free.
How Long Does It Take to See Results?
This isn't traditional SEO. You won't see a slow, steady climb in rankings. Instead, visibility can appear much faster once an AI model re-crawls your newly structured page and deems it a trustworthy source.
Unlike the months it can take to rank organically, you can sometimes see a page get cited in an AI answer within days or weeks of making structural improvements. This is especially true if the page already has some authority. The catch? You have to keep monitoring it. Your citation could just as easily be replaced tomorrow by a competitor's better-structured answer.
Ready to stop guessing and start measuring your AI search performance? AI SEO Tracker shows you exactly where your brand appears in answers from ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. See the prompts your customers are using, track your AI Share of Voice, and get a clear action plan to earn more citations.

