Instead of a list of links, an LLM search engine gives you one direct, synthesized answer.
Think of it this way: a traditional search engine hands you a library catalog. You still have to find the right books, read them, and piece together the answer yourself. An LLM search engine does the reading for you and writes a summary on the spot.
This shift from keyword matching to conceptual understanding changes how we create content.
From Keywords to Concepts
For decades, we’ve played the same game. Search engines like Google work on a simple premise: keyword matching. You type in a query, and the engine digs through its index to find pages with those words. It then uses hundreds of signals to rank those pages. It’s a powerful directory, but you’re still doing the work—clicking, reading, and synthesizing.
An LLM search engine is different. It doesn’t just match keywords; it understands intent.
When you ask a question, the Large Language Model (LLM) powering the engine runs a multi-step process:
- Deconstructs the Query: It breaks down your natural language to figure out what you really mean—the nuance, the context, the goal behind the words.
- Accesses Information: It then pings a real-time web index to find relevant source documents.
- Synthesizes a Response: Instead of just listing the sources, it reads and analyzes information from several top-ranking pages, pulling the most important pieces from each.
- Generates an Answer: Finally, it crafts a new, conversational answer and cites the sources it used.
It's a process less about finding pages and more about creating knowledge on demand. This ability to turn intent into a finished product is a core principle of how modern AI works. A good parallel is seeing what vibe coding is and how it works, as it shows how a fuzzy concept can be translated into a concrete output.
Here’s a clear breakdown of the core differences.
Traditional Search vs. LLM Search: What’s Changed
| Attribute | Traditional Search (e.g., Google) | LLM Search Engine (e.g., Perplexity) |
|---|---|---|
| User Goal | Find a list of relevant links | Get a direct, synthesized answer |
| Core Function | Indexes and ranks web pages | Understands intent and generates new content |
| Result Format | A ranked list of URLs (SERP) | A conversational, paragraph-style response |
| Information Source | Relies on a single click-through link | Synthesizes info from multiple sources at once |
| User Effort | High - user must visit pages and synthesize | Low - the engine synthesizes for the user |
The fundamental user experience is what’s changing. One provides a map; the other offers a guided tour.
Your Audience’s Behavior Is Already Shifting
This isn't just a technological shift; it's a behavioral one. A 2024 report from Brodeur Partners found that 34% of people are already using these platforms daily or almost daily. This isn't a niche trend—it's the new normal.
The user’s goal is different. With Google, the goal is to find a link. With an LLM search engine, the goal is to get an answer.
Your content is no longer just a destination. It's a potential source—a piece of the puzzle the AI uses to construct its answer. This is the foundation of a new discipline focused on AI visibility.
To succeed, you have to shift your strategy from simply ranking to being cited. This is the practice of Generative Engine Optimization. You can learn more about what Generative Engine Optimization is and how it’s reshaping content marketing. This new reality demands a new way of thinking about how AI models see your content.
How LLMs Find and Cite Your Content
An LLM search engine doesn't just "Google" your query. It acts like a research assistant, building an answer from scratch by reading, understanding, and combining information from the best sources it can find in real-time.
Here’s how it works: When you ask a question, the LLM scans a live web index to pull a small handful of top-ranking pages. This is the only part that resembles traditional search. From there, everything changes. The LLM then reads the content on those pages.
It pulls out key facts, data points, and arguments from each source. Then, it synthesizes all that information, weaving it into a single, direct answer. This synthesis step is the entire game. It's the moment the AI decides if your content is valuable enough to become part of its answer.
The diagram below shows this flow from a user's question to a finished, synthesized response.
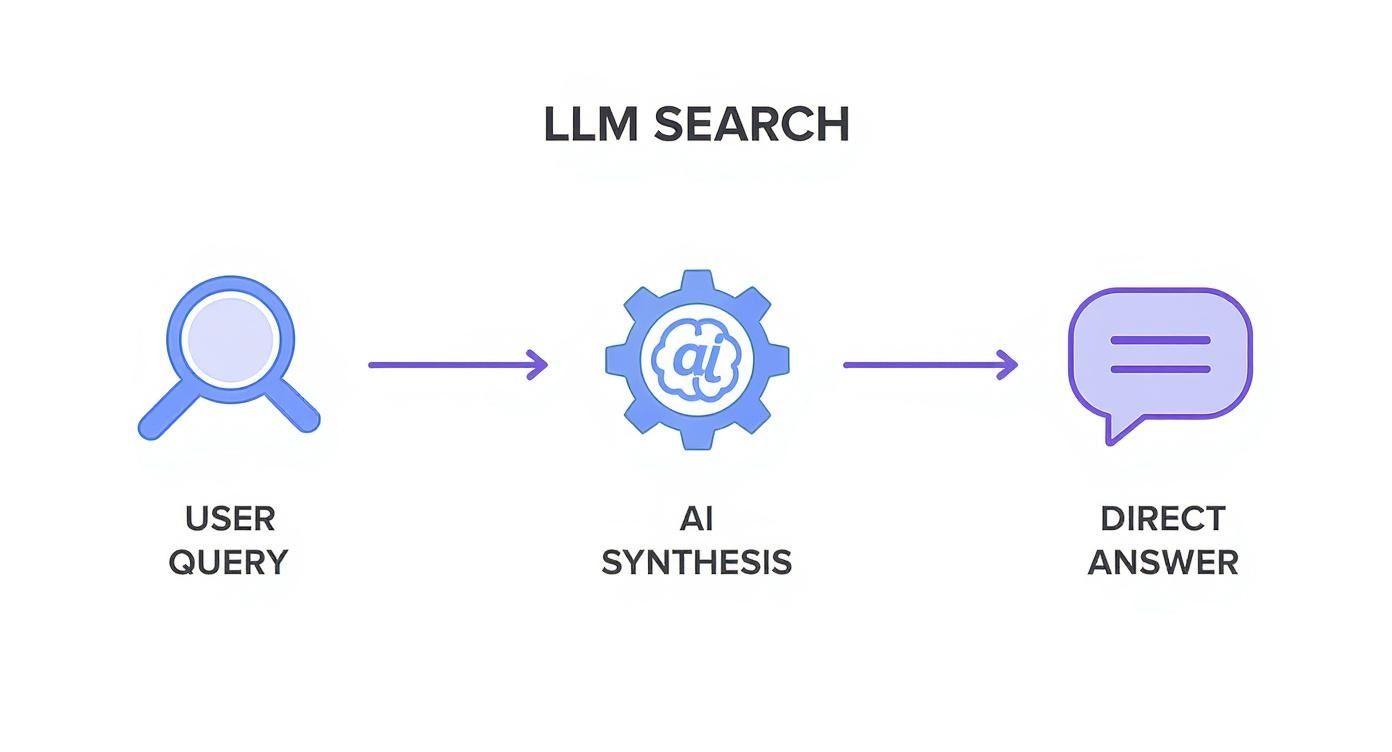
The AI is an intermediary. It consumes content for the user and delivers a final product, not just a list of ingredients.
The Rise of Citation Generation
For marketers, the most critical part of this process isn't the answer itself—it's the citation. Citations are the links back to the original websites the LLM used to build its response.
Getting cited is the new gold standard for SEO.
A citation is a direct endorsement from the AI. It tells the user, "This is a trustworthy source I used to generate your answer." This is far more powerful than just appearing in a list of ten blue links.
An LLM doesn't pick its sources randomly. It actively judges which content is credible enough to reference, prioritizing pages that show strong signals of authority. Learning to optimize for these new factors is now non-negotiable. You can learn more about AI citations and why they matter so much.
What LLMs Look For in a Source
So, how does an LLM decide what’s "citable"? It’s looking for specific signals that tell it your content is reliable, accurate, and easy to understand.
Here are the key signals these models are trained to find:
- Factual Accuracy: The AI prioritizes content with specific numbers, statistics, and claims it can cross-reference. Vague, unsupported statements get ignored.
- Clear Structure: Well-organized content is AI-friendly. Clear headings (H2, H3), lists, and tables make it easier for an AI to parse the structure and understand the information.
- Expert Authorship (E-E-A-T): Content demonstrating Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness gets a massive leg up. This means clear author bios and links to professional profiles are more important than ever.
- Concise Language: An LLM needs to pull out facts fast. Content that gets straight to the point without fluffy intros or jargon is far more likely to be used as a source. Using frameworks from AI for technical writing can help you create the kind of clean, direct content that gets cited.
Think of it this way: the AI is trying to act like a diligent human researcher. It rewards content that is clear, factual, and trustworthy.
Why Citations Matter More Than Clicks
For the last two decades, SEO has been a simple game: climb the rankings. The goal was to land in those top ten blue links. But the rise of the LLM search engine is flipping the entire board over.
The game isn't just about ranking anymore; it's about getting cited.
When a user gets a direct, synthesized answer from an AI, the need to click through to an organic result often disappears. Impressions might be up, but clicks are already tanking for many informational queries. One blogger noted that while his article impressions are higher than ever, his clicks are at the lowest they’ve been in years.
What good is a #1 ranking if nobody clicks it?
From Ranking to Answer Engine Optimization
This new world demands a pivot. We're moving away from traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and toward what is sometimes called Answer Engine Optimization (AEO). The goal is no longer just to attract a click, but to become a foundational source for the AI's generated answer.
An AI citation is a direct endorsement. It’s the engine telling the user, "We built this answer using information from this trusted source." That's a level of authority a simple ranking can't offer.
Sure, this shift might mean less direct traffic for some broad keywords. But the trade-off is almost always worth it. A citation builds brand authority and trust in a way that's more valuable than a fleeting pageview.
The user now directly associates your brand with a correct, helpful answer, cementing you as an expert. This is how you build an audience and influence high-intent users who decide to dig deeper into the AI's sources.
The New Pillars of AI Visibility
To earn these valuable citations, your content needs to be built for an AI to consume and trust. The old signals still matter, but a new set of priorities is taking over.
Here’s what you need to focus on right now:
- Semantic Search Optimization: This is beyond just keywords. It means structuring your content around topics and entities, answering questions directly, and using clear language that a machine can easily parse.
- Structured Data (Schema): Implementing robust Schema markup is no longer a "nice-to-have." It’s how you explicitly tell an LLM search engine what your content is about—whether it's a product, a person, or an organization.
- Citable Facts and Figures: AIs are designed to find and verify information. Embedding explicit, verifiable data points, statistics, and facts into your content is critical. Unsupported claims get ignored; citable data gets rewarded.
This isn't about just writing another blog post. It's about building a repository of citable information. You’re no longer writing just for a human reader; you’re writing for the machine that acts as the gatekeeper. You can check how your content appears to AI with a tool like an AI SEO Tracker.
4 Actionable Tactics to Get Your Content Cited
Optimizing for an LLM search engine isn't about chasing an algorithm. It’s about making your content the most reliable, easiest-to-digest source on the internet.
Think of the AI as a lazy researcher—it will always grab the information that requires the least effort to understand and verify.
Here are four practical tactics you can use to start earning AI citations. They all boil down to clarity, authority, and structure.
1. Answer the Question First
In traditional SEO, we often build suspense with long intros. For an LLM, that is just noise.
The model is scanning for the most direct answer to a user's query. Your most important information needs to be right at the top, immediately after your H2. No fluff.
This "inverted pyramid" approach gives the AI exactly what it’s looking for without forcing it to sift through filler.
- Lead with the conclusion: State the main takeaway in the very first sentence.
- Use simple language: Ditch the jargon and overly complex sentences.
- Format for scanning: Use short paragraphs and bold text to highlight the core answer.
This small shift instantly flags your page as a high-value, direct source.
2. Embed Citable Facts and Data
An LLM is a fact-finding machine. It hunts for verifiable data points to back up the answers it generates. Content without specific, citable facts is basically invisible to an AI.
Vague statements like "many users prefer" get ignored. But specific claims like "78% of users prefer Feature X, according to a 2024 Gartner report" are gold for citation.
Your content needs to become a repository of objective, verifiable information. Every major claim should be backed by a number, a source, or specific evidence.
This turns your content from an opinion piece into a valuable data source the AI can reference with confidence.
3. Implement Robust Schema Markup
Schema markup is structured data you add to your site's code. It's like putting clear labels on your content that tell search engines exactly what each piece of information is.
For an LLM search engine, this isn't optional. Schema removes all ambiguity.
It helps the AI tell the difference between a product name, a price, a review, and an author. This structured context is essential for generating accurate answers.
Start with these key schema types:
- Article Schema: Defines the headline, author, and publication date.
- Organization Schema: Details your company name, logo, and contact info.
- Person Schema: Establishes authoritativeness by linking content to a real expert.
- FAQ Schema: Directly answers common questions in a format an AI can digest.
When you implement schema correctly, you’re spoon-feeding the AI clean, organized data.
4. Prioritize E-E-A-T from the Ground Up
Google's E-E-A-T guidelines (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) are even more important for AI. An LLM has to trust its sources, and E-E-A-T signals are its primary way of measuring that trust.
This isn't just about what's on the page; it's about your entire digital footprint.
- Author Bios: Every article needs a detailed author bio that links to their social profiles and other published work.
- Cite Your Sources: Link out to credible, authoritative sources to back up your claims. This shows you've done your homework.
- Keep Content Fresh: Regularly update your articles with new data. A "last updated" date is a powerful trust signal.
If you want to go deeper, we have a full guide on how to optimize content for AI search that unpacks more of these tactics.
How Winning Brands Optimize for AI Search
Theory only gets you so far. Let's look at two realistic examples of how businesses are adapting their strategies to get cited.
Case Study 1: B2B Tech Blog Earns High-Value Mentions
A B2B SaaS company selling project management software was lost in a crowded market. Their blog content ranked okay, but it never got featured in AI-generated answers for high-intent queries like "best project management tools for small teams."
The problem? A total lack of citable data. Their articles were full of subjective claims. There were no hard numbers an AI could grab onto and trust.
The Solution: Instead of just describing features, they started embedding verifiable data points throughout their content.
- Data-Driven Comparisons: They ditched generic claims like "Our tool offers great collaboration." Instead, they used specific facts: "Our tool supports up to 25 simultaneous users on a single task, compared to the industry average of 10."
- Third-Party Statistics: They backed up their points by including stats from credible sources, like "68% of projects fail due to poor resource planning (PMI, 2024)," and linked to the original reports.
The Outcome: Within two months, their brand started showing up as a cited source in Perplexity and ChatGPT for competitive queries. This led to a 15% increase in branded search volume and a jump in demo requests from people who mentioned seeing them recommended by an AI.
Case Study 2: E-commerce Health Site Drives Product Discovery
A direct-to-consumer wellness brand selling nutritional supplements was struggling. Users were asking AI assistants health questions like "what supplements help with sleep," but the brand's products were nowhere to be found.
Their content was expert-written, but it lacked the technical structure an AI needs to understand the products.
The Solution: The marketing team zeroed in on making their product and article pages machine-readable.
- Implemented Product Schema: They added detailed
Productschema markup to every product page. This included specific fields for ingredients, dosage, price, and health benefits. - Expert Review Schema: For each article, they added
reviewedByschema pointing directly to the medical expert who reviewed the content. This was a clear signal of trustworthiness. - Factual Product Descriptions: They rewrote their product descriptions, replacing marketing fluff with verifiable facts, like "Contains 10mg of Melatonin and 50mg of L-Theanine per serving."
The Outcome: The brand started earning citations in answers to supplement-related questions. Even better, the LLM started linking directly to their product pages when recommending specific ingredients. This drove a 20% lift in direct sales attributed to AI-driven referrals over six months.
You can see how your own pages look to an AI using the AI SEO Page Inspector.
Your Next Steps: An Actionable Plan
Getting your content ready for an LLM search engine is a deliberate process. Instead of trying to do everything at once, focus on building a solid foundation.
Here's your action plan.
Month 1: Foundational Audit
Your first 30 days are about discovery. You need a clear picture of where you stand before you start rewriting anything.
- Run an "AI-Readiness" Content Audit: Pull your top 20 traffic-driving articles. Then, pop their topics into Perplexity or ChatGPT and see if your content gets cited. Score each piece on its use of citable facts and direct answers.
- Upgrade Your Content Briefs: Make AI optimization a non-negotiable part of your process. Update your content brief template to require a minimum of 3-5 verifiable statistics with sources in every article. Mandate a direct, one-paragraph answer at the top.
- Find Your High-Intent Keywords: Brainstorm 10-15 high-value, question-based keywords your customers would ask an AI. Think "what is the best software for..." or "how do I fix X problem." These are your first targets.
Month 2: Content Optimization
With your audit done and new standards set, this month is all about applying what you've learned.
- Optimize 5 Priority Articles: Using the audit from Month 1, rewrite your five highest-potential articles. Weave in citable facts, add clear definitions, and build out robust FAQ and Article schema.
- Create Your First AI-Native Article: Write one brand-new article from scratch using your updated brief. Pick one of the high-intent keywords you found and build the entire piece to be cited.
- Establish E-E-A-T: Make sure every author on your site has a detailed bio with links to their social profiles. If you want to see exactly how your pages look to an AI, a tool like the AI SEO Page Inspector can show you.
Month 3: Measurement and Iteration
You can't improve what you don't measure. The final 30 days are for tracking your progress and refining your approach.
Shift your focus from vanity metrics. The new KPIs are brand mentions, AI citations, and your share of voice for the prompts that matter.
- Track AI Visibility: Use a platform to monitor how often your domain shows up in LLM answers. Are you getting cited more for your target keywords?
- Analyze Performance: Go back to the five articles you optimized. Which ones are earning citations now? What do they have in common? Use those insights to make your content briefs even better.
- Set New KPIs: Establish formal benchmarks for AI citations and share of voice. These metrics need to become a core part of your monthly SEO reporting.
This plan gives you a structured path to adapt to the new world of AI-driven search. It turns a massive shift into a series of concrete steps. To take this foundation to the next level, you'll need to know how to optimize your content for AI search.
What about traditional SEO? Is it dead?
Not at all—but its focus is shifting. Think of it as an evolution.
The core principles still matter. High-quality content, solid backlinks, and good technical health are the foundation. An LLM search engine still needs a way to find your page, and it leans on those traditional ranking signals to do it.
The real change is the end goal. It's no longer just about ranking #1. It's about getting cited. This means adding a new layer of optimization focused on clarity, structure, and citable facts.
Which is more important: clicks or citations?
This boils down to your goals. Clicks drive traffic right now. Citations build long-term authority and brand trust. A citation is a direct endorsement from the AI, stamping your brand as the definitive source.
For someone deep in the buying cycle, a single citation can be more valuable than a hundred low-intent clicks. It delivers high-quality traffic from users who are already convinced of your expertise.
The best strategy balances both, but the future belongs to citation-worthy content.
Next Step: See where your content shows up in AI answers. AI SEO Tracker gives you the data you need to monitor citations, analyze competitor visibility, and build a winning strategy for this new era of search. Find out how often you're being cited and start optimizing today at https://aiseotracker.com.

